Hands-On: 3-way Handshake Process
Lab ID: CCNA-IP-W05-L1-TCP-UDP-PT-v1
File Name: CCNA-IP-W05-L1-TCP-UDP-PT-v1.pkZ
Lab Objective
Understand and observe how the TCP 3-way handshake works in data transmission using Packet Tracer. You will test how TCP establishes a reliable connection through the SYN, SYN-ACK, and ACK sequence before any data is sent.
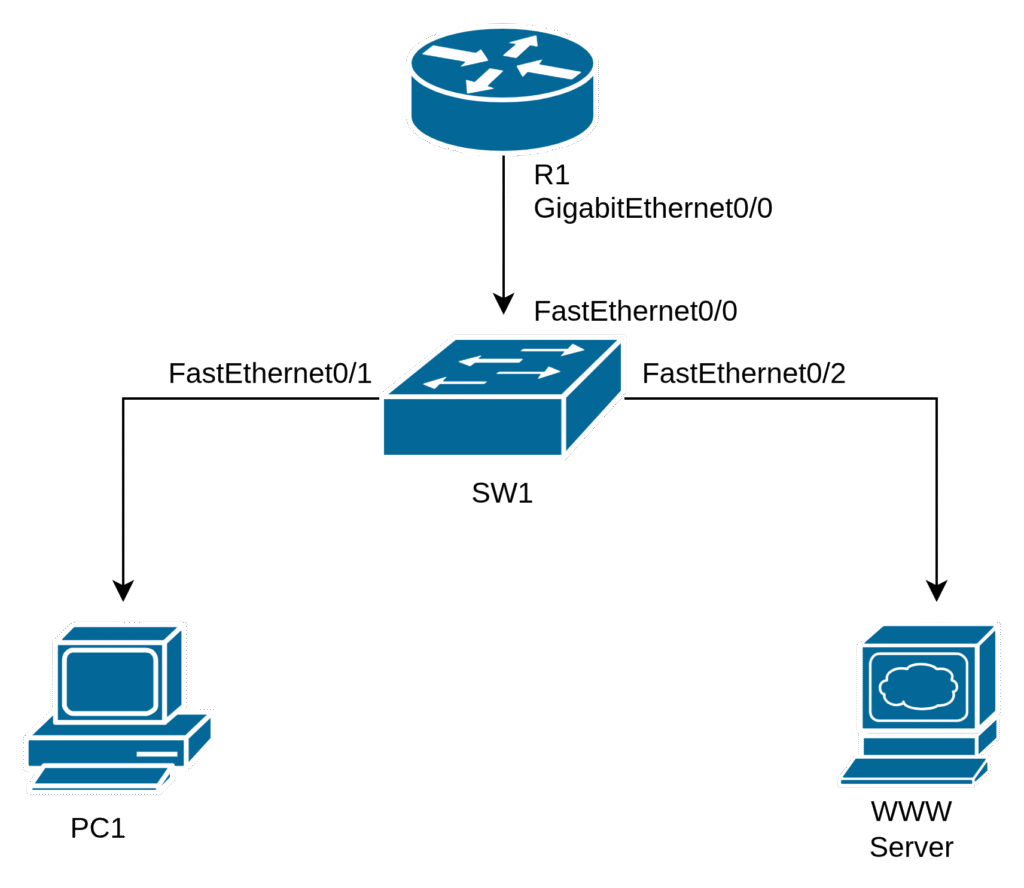
Lab Topology
The lab topology displays information about the network devices in the lab.
Key Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
enable | Enters privileged EXEC mode (also known as “enable mode”) to access higher-level commands. |
configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode, allowing you to make system-wide changes to the device. |
hostname <name> | Assigns a custom name to the device (e.g., hostname R1). |
interface <type> <number> | Enters interface configuration mode for a specific port (e.g., interface g0/0). |
ip address <ip> <mask> | Assigns an IP address and subnet mask to the selected interface. |
no shutdown | Activates (brings up) the interface — interfaces are administratively down by default. |
show ip interface brief | Displays a summary of all interfaces, showing IP addresses and their up/down status. |
ping <ip-address> | Sends an ICMP Echo Request to test connectivity with another device and verify reachability. |
IP Addresses
The IP addresses and subset masks used in this lab are shown in the tables below:
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | NIC | 192.168.10.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.10.1 |
| WWW Server | NIC | 192.168.10.20 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.10.1 |
| R1 | G0/0 | 192.168.10.1 | 255.255.255.0 | — |
Lab Tasks
Task 1 —
- Open Cisco Packet Tracer. Select the network devices shown in the topology diagram (e.g., router, switch, PCs, and server). Place the devices on the workspace and arrange them according to the network topology.
- Assume that Auto-MDIX is disabled, so you must choose the appropriate cable types manually: Use straight-through cables to connect PCs and servers to switches. Use cross-over cables for switch-to-switch or router-to-switch connections (if required). Connect each device to its corresponding interface as indicated in the topology diagram.
- Using the CLI, assign the appropriate hostname to each device according to the network diagram.
Task 2 —
- Configure all devices with their designated IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways according to the network addressing plan.
- Tip: After configuration, make sure all interfaces are in the up/up state before proceeding with connectivity tests.
- Configuring HTTP and HTTPS Services on a WWW Server in Packet Tracer. You don’t know how to do it? Well… figure it out all by yourself, buddy!
Task 3 —
- After completing the IP configuration, verify basic connectivity: From PC1 ping R1 (192.168.10.1) and WWW Server (192.168.10.20). Did the ping test work successfully?
- Next, open the Web Browser on PC1 and type the server’s IP address in the address bar (192.168.10.20). If the HTTP service is enabled on the server, you should see the default web page — confirming that TCP communication is working correctly.
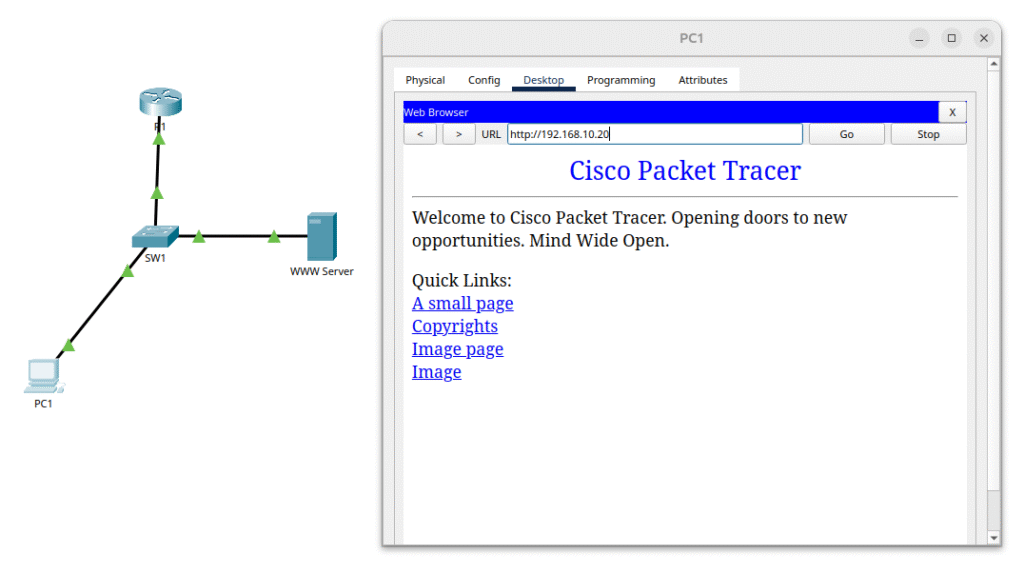
- Verify the TCP 3-Way Handshake in Simulation Mode: Switch Packet Tracer to Simulation Mode (bottom-right corner). In the Event List Filters, uncheck “Show All/Other” and select only TCP to focus on TCP traffic. On PC1, open the Web Browser and type the server’s IP address (http://192.168.10.20). Watch the Simulation Panel as the packets appear.
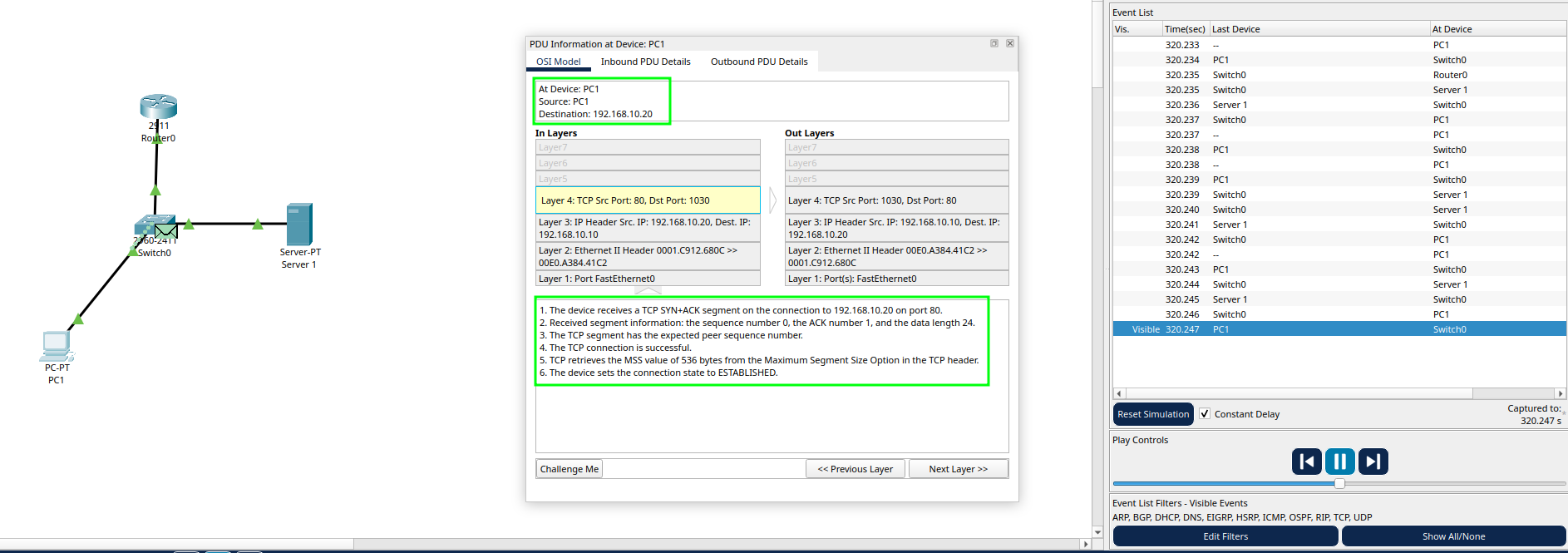
****
Keep Practicing!
This activity is part of the From Zero To CCNA learning path. fromzerotoccna.com
