The Fast Evolution of Spanning Tree in Cisco Networks
Primary Difference Between PVST+ and Rapid-PVST+
In Cisco switching environments, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a critical technology used to prevent Layer 2 loops. Cisco has developed several STP implementations to improve performance and scalability in VLAN-based networks. Two of the most common Cisco implementations are PVST+ (Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus) and Rapid-PVST+ (Rapid Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus).
The primary difference between PVST+ and Rapid-PVST+ is the convergence mechanism and speed when the network topology changes. While both protocols operate on a per-VLAN basis, they are built on different IEEE standards and behave very differently during failures and recoveries.
Overview of PVST+
PVST+ is Cisco’s enhancement of the original IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol. It allows a separate spanning-tree instance for each VLAN, which gives network engineers better control over traffic paths.
Key Characteristics of PVST+
- Based on IEEE 802.1D
- One spanning-tree instance per VLAN
- Uses classic STP timers
- Slow convergence
- Supported on Cisco switches for legacy compatibility
PVST+ relies heavily on timers to transition ports between states. When a topology change occurs, ports must move through multiple states before forwarding traffic again.
PVST+ Port States
- Blocking
- Listening
- Learning
- Forwarding
Each transition uses default timers:
- Forward Delay: 15 seconds
- Max Age: 20 seconds
As a result, full convergence can take 30 to 50 seconds.
PVST+ Logical Flow Diagram
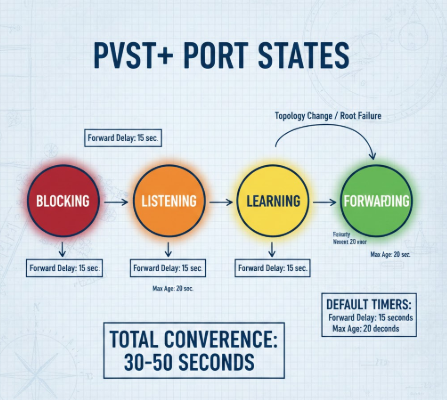
This diagram shows the timer-based progression used by PVST+.
Overview of Rapid-PVST+
Rapid-PVST+ is Cisco’s per-VLAN implementation of IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It was designed to solve the slow convergence problem of 802.1D.
Key Characteristics of Rapid-PVST+
- Based on IEEE 802.1w
- One spanning-tree instance per VLAN
- Event-driven convergence
- Very fast recovery
- Default STP mode on modern Cisco switches
Rapid-PVST+ does not wait for timers to expire. Instead, it uses handshake mechanisms between switches to quickly determine whether a port can safely transition to forwarding.
Rapid-PVST+ Port Roles and States
Rapid-PVST+ introduces new port roles and simplifies states.
Port Roles
- Root
- Designated
- Alternate
- Backup
- Edge
Port States
- Discarding
- Learning
- Forwarding
Ports can move to forwarding almost immediately when conditions are met.
Rapid-PVST+ Logical Flow Diagram
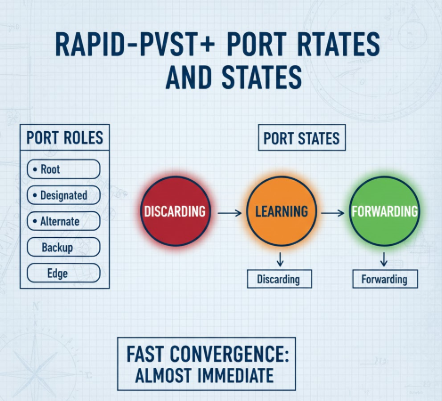
This diagram shows the simplified and faster state transitions used by Rapid-PVST+.
Primary Difference
The primary difference between PVST+ and Rapid-PVST+ is:
PVST+ relies on timers for convergence, while Rapid-PVST+ relies on active handshakes and immediate decision-making.
This results in a major difference in convergence speed.
- PVST+: 30–50 seconds
- Rapid-PVST+: Less than 1–3 seconds in most cases
Cisco Network Impact
In real Cisco networks, slow convergence can cause:
- Voice call drops
- Application timeouts
- Routing protocol instability
- User connectivity issues
Rapid-PVST+ significantly reduces these risks and is suitable for:
- Enterprise campus networks
- Data center access layers
- Environments with frequent topology changes
Troubleshooting Tools and Commands
Cisco provides several tools to verify and troubleshoot both protocols.
Verify Spanning Tree Mode
show spanning-tree summaryVerify Per-VLAN Status
show spanning-tree vlan <vlan-id>Check Rapid-PVST+ Operation
show spanning-tree detailEnable Rapid-PVST+
spanning-tree mode rapid-pvstIdentify Edge Ports
show spanning-tree interface <interface-id> detail*Correct edge port configuration is critical for fast convergence.
Best Practices in Cisco Environments
- Use Rapid-PVST+ as the default STP mode
- Configure PortFast on access ports
- Avoid mixing legacy 802.1D devices when possible
- Monitor topology changes using logs and SNMP
- Document root bridge placement per VLAN
PVST+ and Rapid-PVST+ both provide per-VLAN loop prevention in Cisco networks. However, they are not equivalent in performance.
- PVST+ is based on legacy STP and converges slowly
- Rapid-PVST+ is based on RSTP and converges almost instantly
For modern Cisco networks, Rapid-PVST+ is the correct and recommended choice unless backward compatibility is required.
Questions, comments, or just wanna drop a ‘hey’?
Email: fromzerotoccna@gmail.com
