Comprehensive Guide to Operating Cisco IOS Software
Unlocking the Full Potential of Cisco IOS for Smarter and Stronger Networks.
First Listen: let your ears lead the way before your mind takes notes.
📻 FZ2CCNA Radio:
Then read: let your eyes explore before your mind starts to explain.
The First Time You Meet IOS
Picture this: you’re standing in a small server room, fluorescent lights buzzing above you, a rack of Cisco equipment in front of you, fans humming like a chorus of tiny hair dryers. Someone hands you a laptop, a blue console cable, and says, “Alright, you’re in charge.”
You plug in the cable, open a terminal program, and—like magic—a black screen appears with a blinking cursor.
That’s your first handshake with Cisco IOS — the Internetwork Operating System. It’s the “brain” and the voice of every Cisco router and switch. Without it, your hardware is just a silent box with blinking lights. With it, the box can route data across continents, connect offices, and keep businesses running.
Note: Cisco IOS is not the same as Apple’s iOS. One runs billion-dollar corporate networks; the other lets you play Candy Crush while waiting for your coffee. If you try to “update” a Cisco router from the App Store, you’re going to have a very bad day.
IOS in Plain Language
If Cisco IOS were a person, it would be that one coworker who knows exactly how everything works, is never wrong, but only responds if you use the right words. It doesn’t do small talk. You type a command—it gives you results. You type the wrong thing—it replies “Invalid input detected” and waits for you to try again.
Its main jobs:
- Routing: Make sure data gets where it’s supposed to go.
- Switching: Direct traffic inside your network.
- Security: Keep out intruders.
- Management: Let you see and control the whole system.
How You “Knock on the Door” of IOS
Getting into IOS is like entering a house with multiple entrances. Some are safer, some are faster, and some are only for emergencies:
- Console port — like a back door used when nothing else works; accessed with a console cable.
- SSH — the secure main entrance.
- Telnet — the old front door; functional but unsafe.
The Console Port — The Backstage Pass
The console port is your direct access point. Using a console cable and terminal software (PuTTY, Tera Term, etc.), you can access the device even when:
- The network is down.
- The device is brand new with no configuration.
Pro tip: Always carry a console cable—it’s your universal master key.
Telnet — The Old Front Door
- Connects via port 23.
- Sends all data (including passwords) in plain text.
- Insecure; only safe for lab environments like Cisco Packet Tracer.
SSH — The Secure Entrance
- Connects via port 22.
- Encrypts all communication.
- Recommended for all real-world network access.
IOS Modes — Levels of Trust
Cisco IOS has “modes” that control how much you can do. Think of them as building access levels:
- User EXEC Mode (
>) — The lobby.- Can run basic show and ping commands.
- No configuration changes allowed.
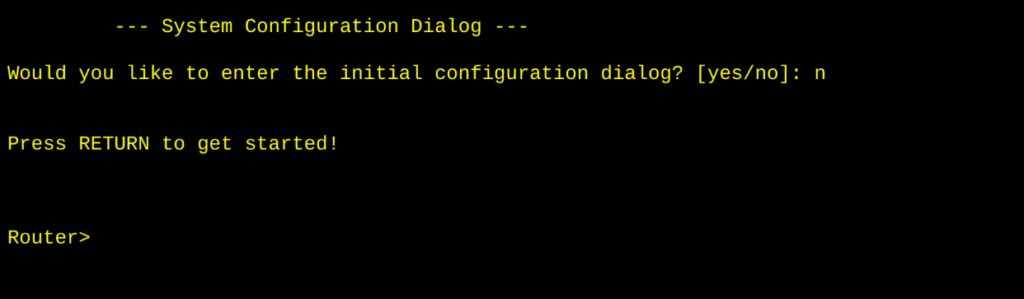
- Privileged EXEC Mode (
#) — The control room.- Enter with:
enable. - Can run advanced commands and view sensitive info.
- Should always be password-protected.
- Enter with:

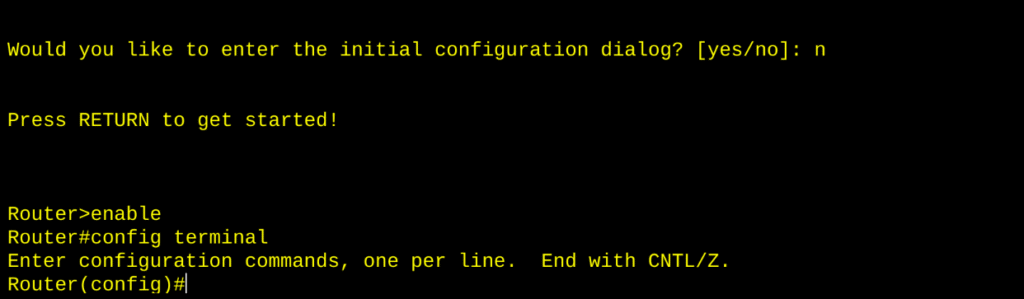
- Global Configuration Mode (
(config)#) — The master controls.- Enter with:
configure terminal. - Make system-wide changes (IP settings, hostname, protocols).
- Must save changes with:
copy running-config startup-config.
- Enter with:
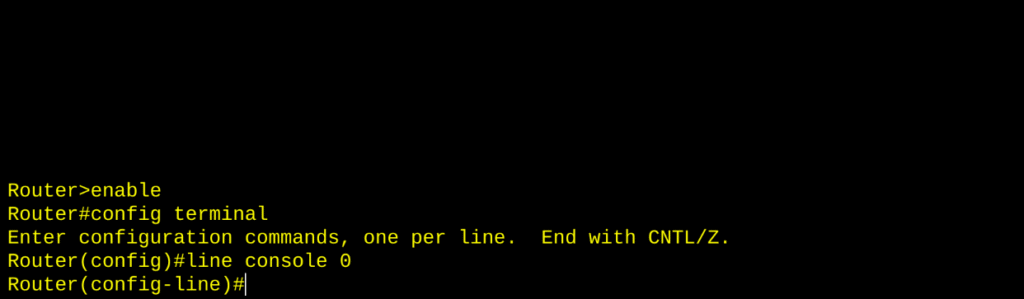
- Specific Configuration Modes — The workbenches.
- Interface Config (
(config-if)#) — Set IPs, enable/disable ports.
- Interface Config (

- Line Config (
(config-line)#) — Control login methods, console/SSH access.
Essential IOS Commands
show running-config— View the current configuration.copy running-config startup-config— Save changes permanently.show ip interface brief— Quick status of interfaces and IPs.hostname <name>— Assign device name.exit— Move back one mode level.
Best Practices
- Save often — Always store changes to prevent loss on reboot.
- Document interfaces — Use
descriptionfor clarity. - Secure access — Prefer SSH over
Telnet; use strong passwords. - Change incrementally — Test after each change.
Exam Tips
- Always check the prompt to know your current mode.
- Move between modes deliberately—don’t configure from the wrong level.
- In simulations, take your time and plan before entering commands.
Understanding IOS Memory Types
To work effectively with IOS, you need to know where configurations are stored:
| Memory Type | Purpose | Volatility |
|---|---|---|
| RAM | Stores the running configuration and routing tables | Volatile — cleared on reboot |
| NVRAM | Stores the startup configuration | Non-volatile — retained after reboot |
| Flash | Stores the IOS image and other files | Non-volatile — retained after reboot |
| ROM | Stores the bootstrap program | Non-volatile |
Example:
When you run copy running-config startup-config, you’re copying the configuration from RAM (current) to NVRAM (saved).
IOS Mode Navigation Quick Reference
| Mode | Prompt | How to Enter | How to Exit |
|---|---|---|---|
| User EXEC | > | Login | exit |
| Privileged EXEC | # | enable | disable |
| Global Configuration | (config)# | configure terminal | exit |
| Interface Configuration | (config-if)# | interface <type> <number> | exit |
| Line Configuration | (config-line)# | line <type> <number> | exit |
The Takeaway
Cisco IOS is precise, predictable, and reliable. Learn its modes, prompts, and core commands, and it stops feeling like a black box and starts becoming your most dependable teammate. In the lab, Packet Tracer is your training ground — a safe space to try, break, and fix without fear.
Every command you type, every configuration you test, chips away at the mystery and builds real-world confidence. By the time you face the CCNA exam, you won’t be meeting IOS for the first time — you’ll be catching up with an old friend who’s helped you through countless practice runs.
What Did You Learn Today?
Let’s Find Out!
Instructions
- Select the correct answer for each technology concept.
- All questions pertain directly to the networking technologies explained.
- After answering, click “See Result” to see your score and feedback.
[Return to CCNA Study Hub] — Next Stop: [Section 2 | LAN Basics] …Currently Buffering… Available Soon!
