What You Just Saw in Network Diagram Form | Part Two
Make sense of Cisco diagrams by mastering basic topology symbols.
First Listen: let your ears lead the way before your mind takes notes.
📻 FZ2CCNA Radio:
Then read: let your eyes explore before your mind starts to explain.
What Are Cisco Topology Icons?
Imagine you’re looking at a subway map for the first time. There’s no explanation, just lines and symbols — but somehow, you get it. That circle is a station. That triangle? A transfer point. That squiggly line? Maybe it’s under construction (good luck).
Now apply that logic to computer networks. In the world of networking, Cisco Topology Icons are the universal symbols we use to draw and understand network diagrams.
These icons are like the stickers on a map that help us figure out what device is what — without reading a single line of code. Each icon represents a specific type of hardware or function: routers, switches, firewalls, cloud connections, access points, you name it.
In short: Cisco Topology Icons are the cartoon language of network engineers — simple, visual, and powerful.
Why Are These Icons Important?
Let’s get real for a second: no one wants to read a giant paragraph that says:
“This is a layer 3 router that connects to a layer 2 switch that distributes traffic to an access point that connects wirelessly to the end device…”
No thanks. Just show me a picture!
That’s where icons come in. Here’s why they matter:
- Quick understanding: One glance and you know what’s going on.
- Consistency: Everyone speaks the same visual language, from IT interns to senior network architects.
- Exam relevance: In CCNA, you’ll see these icons in packet tracer labs, multiple-choice questions, and drag-and-drop simulations.
- Navigation: Icons help you mentally “walk through” a network and understand how traffic flows.
Without icons, network diagrams are like trying to find a friend’s house in a neighborhood where every street sign is missing and every house looks the same.
Categories of Icons
Let’s break this down like a pizza: different slices, same dish.
Cisco has many icon categories, but for CCNA we’ll focus on the four main ones.
LAN (Local Area Network)
These are your day-to-day stars — the ones you plug into and configure. These are connections inside your building or campus.
| Icon | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
 | Router | Routes traffic between networks. Think of it as the GPS. |
 | Switch Layer 2 | Connects devices inside the same network. Like a power strip for data. |
 | Switch Layer 3 | A switch that also knows how to route between networks — like a switch with a router’s brain. |
 | PC | End device used by humans. (Yes, the ones that break all the time.) |
| | Firewall | A security device that controls what traffic is allowed in or out of a network. |
| | Server | Provides services to other devices — like a vending machine of data. |
| IP Phone | A phone that uses the internet (IP) to make and receive calls instead of traditional phone lines. | |
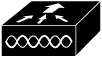 | WLAN Controller | A device that manages multiple wireless access points in a network, centralizing configuration and security. |
 | LWAPP (Lightweight Access Point Protocol) | A protocol that lets access points communicate with a central WLAN controller for simplified management and control. |
| Access Point | A device that connects wireless devices to a wired network using Wi-Fi. | |
 | Hub | Dumb switch that copies traffic everywhere. Mostly obsolete. |
| ______________ | Ethernet Link | A wired connection that lets two devices exchange data in a network. |
 | Bridge | Connects two LAN segments. Mostly obsolete. |
WAN (Wide Area Network)
Used when you’re dealing with the “big world” outside your office.
| Icon | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud | Represents the Internet or “we don’t care what’s inside” network. | |
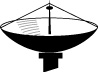 | Satellite | For satellite-based connections (rare but cool). |
 | Serial Link | A leased line — think long-distance private connection. |
Security
Things that keep the bad guys out.
| Icon | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
 | Firewall | A security device that controls what traffic is allowed in or out of a network. |
| VPN Gateway | Opens secure tunnels to other networks. | |
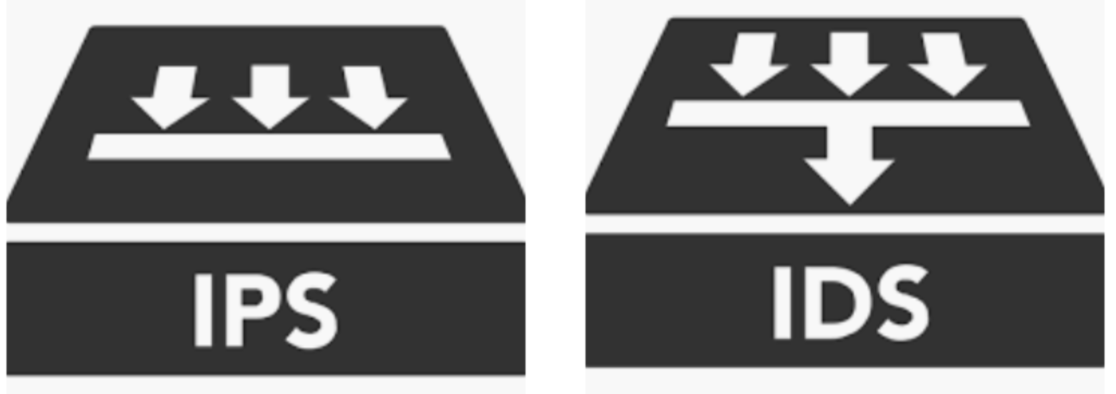 | IDS/IPS | Watches network traffic like a hawk. |
Wireless
Because not everything needs cables (except your sanity).
| Icon | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
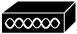 | Access Point (AP) | A device that connects wireless devices to a wired network using Wi-Fi. |
  | Wireless Device | Your phone, tablet, laptop, etc. |
 | Antenna | Boosts or transmits wireless signals. |
Most Common Icons You’ll See in CCNA Labs
In real CCNA labs — whether Packet Tracer or real hardware — you’ll deal mostly with:
- Router
- Switch
- PC
- Access Point
- Firewall
- Cloud (Internet)
Focus on recognizing these fast. If you’re in a simulation and confuse a switch for a router… that’s like mistaking the oven for the fridge in a cooking exam.
How to Memorize Them (Even If You Have a Terrible Memory)
Look, not everyone is good at memorizing stuff. So let’s cheat a little (ethically!):
Router
Think of it like a highway exit sign.
Routers tell traffic which way to go to reach other networks — just like highway signs direct cars to different cities. It’s not the road; it’s the guide.
Switch
Like a smart power strip for data.
It connects multiple devices and only sends data to the right one — no wasting electricity (or bandwidth) on others.
Firewall
Like a security guard with a clipboard.
It checks every visitor (packet) and only lets in the ones on the list. Sketchy data? Blocked.
Access Point
Like a Wi-Fi sprinkler connected to a garden hose.
It sprays wireless signal all around so your devices can “drink” data — but it still needs to be connected to a hose (Ethernet cable) to get the water (network connection) from the source (the switch).
Cloud (Internet)
Like sending a letter to Santa.
You drop your data in and trust it gets delivered, but… who really knows how? That’s the cloud.
IP Phone
Like a regular office phone but speaks digital.
It doesn’t use phone lines — it talks over the network just like a PC.
VPN Gateway
Like a secret tunnel entrance.
Lets you safely enter a remote network from far away — and keeps eavesdroppers out.
WLAN Controller
Think of it like the school principal for all Wi-Fi access points.
It makes sure every AP behaves, follows the rules, and doesn’t fight with others.
LWAPP
Like a walkie-talkie signal between AP and the controller.
The AP doesn’t decide anything — it just radios in for instructions.
Repetition is key: The “Light Switch Icon Drill
- Stick a tiny printout of one CCNA icon (router, switch, firewall, or cloud) next to a light switch you use every day.
- Every time you toggle the switch, say the icon’s name and one function out loud (“That’s a router—directs traffic between networks”).
It takes under a second, happens dozens of times daily without extra effort, and by exam day you’ll recognize each icon—and what it does—instantly.
Real-World Best Practices for Reading and Using Network Diagrams
✅ Do:
- Start reading diagrams from the core to the edge: core routers → switches → access → end devices.
- Use standard icons (don’t invent your own, you rebel).
- Add labels: IPs, VLANs, device names.
❌ Don’t:
- Mix WAN and LAN icons.
- Overcrowd the diagram.
- Forget to document — you’ll forget what that one unlabeled icon was two weeks later.
Pro tip: In real jobs, network diagrams are often out-of-date. Learn to question everything — like a toddler with a screwdriver.
How They Show Up in the CCNA Exam
On the CCNA exam (200-301), these icons show up in:
- Drag-and-drop questions
(Match icon to function or name.) - Simulations
(You’ll see a mini topology with these icons and have to configure something.) - Topology-based multiple choice
(Interpret what’s happening in a network diagram.)
🔑 You don’t need to draw them, but you do need to recognize them at a glance.
Final Tips and What to Memorize for the Test
What to memorize:
- All of them.
- The function of each device.
- How to read a basic topology.
Exam Tips:
- Don’t panic if you see a new icon — hover or click on it if possible.
- Trust your gut: if it has antenna waves, it’s probably wireless.
- If it looks like a box with many arrows, it’s probably a switch.
Extra trick:
Create a 1-page cheat sheet of icons and stick it on your wall. Review it every day for a week. By the 3rd day, you’ll remember them like your phone’s unlock pattern.
Summary
Cisco Topology Icons are the network engineer’s alphabet. If you learn to read them, you can read and build networks anywhere — from a tiny home office to a global data center.
Like learning a new language, it starts slow. But once you get the basics, it becomes second nature.
Drawing your own topologies like a pro, or at least pretending until you pass the exam.
Next Stop: [Section 1 | Ignite] + [Packet Tracer]
